AI system development: CNIL’s recommendations to comply with the GDPR
05 January 2026
To help professionals reconcile innovation and respect of people’s rights, the CNIL has published its first recommendations on the application of the GDPR to the development of artificial intelligence systems. Here's what you need to know.
Designers and developers of AI systems often report to the CNIL that the application of the GDPR is challenging for them, in particular for the training of models.
The misconception that the GDPR would prevent AI innovation in Europe is false. However, we must be aware that training datasets sometimes include “personal data”, i.e. data on real people. The use of such data poses risks to individuals, which must be taken into account, in order to develop AI systems under conditions that respect individuals’ rights and freedoms, including their right to privacy.
In addition to the how-to sheets and this synthesis, the CNIL provides professionals with a checklist of key points to review.
Scope of the recommendations
Which AI systems are concerned?
These recommendations adress the development of AI systems involving the processing of personal data (for more information on the legal framework, see how-to sheet 1). The training of AI systems regularly requires the use of large volumes of information on natural persons, known as "personal data".
The following are concerned:
- Systems based on machine learning;
- Systems whose operational use is defined from the development phase and general purpose AI (GPAI) systems that can be used for various applications;
- Systems for which the learning is done “once and for all” or continuously, e.g. using usage data for its improvement.
What are the steps involved?
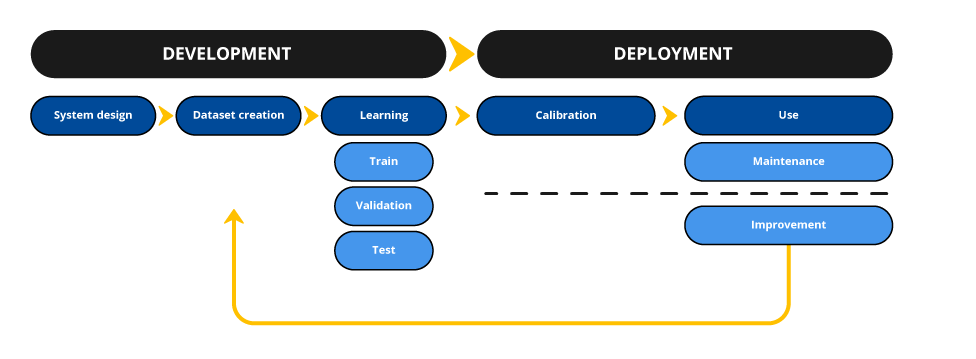
These recommendations concern the development phase of AI systems, not the deployment phase.
The development phase includes all the steps prior to the deployment of the AI system in production: system design, dataset creation and model training.
How do these recommendations relate to the European AI Act?
The recommendations take into account the EU Artificial Intelligence Act adopted in the summer 2024. Indeed, where personal data is used for the development of an AI system, both the GDPR and the AI Act apply. CNIL's recommendations have therefore been drawn up to supplement them in a consistent manner regarding data protection.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 0
Step 1: Define an objective (purpose) for the AI system
The principle
An AI system based on the exploitation of personal data must be developed with a “purpose”, i.e. a well-defined objective.
This makes it possible to frame and limit the personal data that can be used for training, so as not to store and process unnecessary data.
This objective must be determined, or established as soon as the project is defined. It must also be explicit, i.e. known and understandable. Finally, it must be legitimate, i.e. compatible with the organisation’s tasks.
It is sometimes objected that the requirement to define a purpose is incompatible with the training of AI models, which may develop unanticipated characteristics. The CNIL considers that this is not the case and that the requirement to define a purpose must be adapted to the context of AI, without, however, disappearing, as the following examples show.
In practice
There are three types of situations.
You clearly know what the operational use of your AI system will be
In this case, this objective will be the purpose of the development phase as well as the deployment phase.
However, this is more complex when you are developing a general purpose AI system that can be used in various contexts and applications or when your system is developed for scientific research purposes.
For general purpose AI systems
You cannot define the purpose too broadly as, for example, "the development and improvement of an AI system". You will need to be more precise and refer to:
- the "type" of system developed, such as, for example, the development of a large language model, a computer vision system or a generative AI system for images, videos, sounds, computer code, etc.;
- the technically feasible functionalities and capabilities.
Good practice:
You can give even more details about the objective pursued, for example by determining:
- the foreseeable capacities most at risk;
- functionalities excluded by design;
- the conditions of use of the AI system: the known use cases of the solution or the conditions of use (dissemination of the model in open source, marketing, availability trough SaaS or API, etc.).
For AI systems developed for scientific research purposes
You can define a less detailed objective, given the difficulties of defining it precisely from the beginning of your work. You can then provide additional information to clarify this goal as your project progresses.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 2
Step 2: Determine your responsibilities
The principle
If you use personal data for the development of AI systems, you need to determine your liability within the meaning of the GDPR. You can be:
- data controller: you determine the purposes and means, i.e. you decide on the "why" and "how" of the use of personal data. If one or more other bodies decide with you on these elements, you will be joint controllers for the processing and will have to define your respective obligations (e.g. through a contract).
- data processor: you process data on behalf of the “data controller”. In this case, the latter must ensure that you comply with the GDPR and that you process the data only on its instructions: the law then provides for the conclusion of data processing agreement.
In practice
The European AI Act defines several roles:
- an AI system provider developing or having developed a system and placing it on the market or putting it into service under its own name or trade mark, whether for a fee or free of charge;
- importers, distributors and users (also known as deployers) of these systems.
Your degree of responsibility depends on a case-by-case analysis. For example:
- If you are a provider at the initiative of the development of an AI system and you constitute the training dataset from data you have selected for your own account, you can be qualified as a data controller.
- If you are building the training dataset of an AI system with other data controllers for a purpose that you have defined together, you can be referred to as joint controllers.
- If you are an AI system provider, you can be a subcontractor if you are developing a system on behalf of one of your customers. The customer will be responsible for processing if he determines the purpose but also the means, the techniques to be used. If it only gives you one goal to achieve and you design the AI system, you are data controller.
- If you are an AI system provider you can use a service provider to collect and process the data according to your instructions. This service provider will be your subcontractor. This is the case, for example, of the provider that has to set up a training dataset for an AI system provider that tells it precisely how it has to be developed.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 3
For the rest:
- If you are a data controller, all the following steps are of direct concern to you, and you are responsible for ensuring compliance.
- If you are a data processor, your main obligations are the following:
- Ensure that a contract for the processing of personal data has been concluded with the data controller and that it complies with the regulation;
- Strictly follow the instructions of the data controller and do not use the personal data for anything else;
- Strictly ensure the security of the data processed;
- Assess compliance with the GDPR at your level (see next steps) and alert the controller if you feel there is a problem.
Step 3: Define the "legal basis" that allows you to process personal data
The principle
The development of AI systems involving personal data will need to have a legal basis that allows you to process this data. The GDPR lists six possible legal bases: consent, compliance with a legal obligation, the performance of a contract, the performance of a task carried out in the public interest, the safeguarding of vital interests of the data subjects, the pursuit of a legitimate interest.
Depending on the legal basis chosen, your obligations and the rights of individuals may vary, which is why it is important to determine it upstream and indicate it in the data privacy policy.
In practice
Identify the appropriate legal basis
You need to ask yourself about the most appropriate legal basis for your situation.
If you collect data directly from individuals and they are free to accept or refuse without harm (such as giving up the service), consent is often the most appropriate legal basis. According to the law, it must be free, specific, enlightened and unambiguous.
Gathering consent, however, is often impossible in practice. For example, when you collect data accessible online or reuse an open source dataset, without direct contact with data subjects, other legal bases will generally be more suitable:
- Private actors will have to analyse whether they comply with the conditions in order to rely on legitimate interest. To do so, they must justify that:
- the interest pursued is legitimate, that is to say, legal, precisely and genuinely defined;
- the personal data are really necessary for the training of the system, because it is not possible to use only data which do not relate to natural persons or anonymised data;
- the use of such personal data does not lead to a “disproportionate impact” with the privacy of individuals. This is assessed on a case-by-case basis, depending on what is revealed by the data used, which may be more or less private or sensitive, and what is done with the data.
- the interest pursued is legitimate, that is to say, legal, precisely and genuinely defined;
- Public actors must verify whether the processing is in line with their public interest mission as provided for by a law (e.g. a law, decree, etc.) and whether it contributes to it in a relevant and appropriate way.
Example: the French pôle d'expertise de la régulation numérique (PEReN) is authorised on this basis to reuse publicly available data to carry out experiments aimed in particular at designing technical tools for the regulation of operators of online platforms.
The legal bases of the contract and the legal obligation may be used more exceptionally, if you demonstrate how your processing is necessary to meet the performance of the contract or pre-contractual measures or a (sufficiently precise) legal obligation to which you are subject.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 4
Relying on legitimate interest
Legitimate interest is one of the most commonly used legal bases for developing AI systems, particularly by private entities. The “interest” refers to the benefit that the data controller or third parties derive from the development of the AI system.
Using legitimate interest as a legal basis is subject to three conditions:
-
The interest pursued must be "legitimate"
The interest must be lawful under applicable legislation (including regulations beyond the GDPR, such as the EU AI Act), and it must be clearly and specifically defined. It should also be linked to your mission and activities.
Examples of interests generally considered legitimate: conducting scientific research, facilitating public access to certain types of information, offering a conversational assistant service to users, or developing an AI system for detecting fraudulent content or behavior.
A commercial interest may qualify as legitimate provided it is lawful and the processing is necessary and proportionate.
-
The processing must be necessary
The pursued interest cannot be achievable by less intrusive means in terms of privacy. The development of the system is necessary to reach the intended objective.
This necessity should be assessed in light of the data minimization principle (see “Step 5: Minimize the personal data you use”).
-
The processing must not cause a disproportionate impact on individuals’ privacy
The data controller must weigh the expected benefits of the processing against its potential impact on the rights and freedoms of the individuals concerned. If needed, safeguards must be put in place to reduce those risks and protect individuals’ rights.
Considering individuals’ reasonable expectations
The use of their data should not come as a surprise to individuals. Several factors must be considered when relying on legitimate interest to process data:
- for data collected directly from individuals: consider the relationship with the individual, the context of the data collection, the nature of the service, privacy settings, and whether the data processing serves only the individual or aims at improving the service overall;
- for the reuse of online data: the publicly accessible nature of the data the context and nature of the source websites (e.g., social networks, online forums, open data platforms), the type of content published, and the relationship between the individual and the organization publishing the data. Processing will not fall within reasonable expectations of the individuals if you include websites in your data collection that have set restrictions (e.g., terms of use, robots.txt files, CAPTCHA protections).
Please note: individuals may be aware that some data they post online could be viewed, collected, or reused by third parties. However, they do not expect this to happen in every situation or for all types of publicly available personal data.
Safeguards to limit the impact of processing
Safeguards can reduce the amount of personal data collected or retained, help individuals maintain control over their data, and mitigate risks during use. These measures should be proportionate to the risks and tailored to each phase of system development. For example:
- ensuring timely anonymization of collected data or, if not feasible, applying pseudonymization;
- implementing measures to reduce the risk of model memorization, thereby lowering the chances of data extraction or regurgitation;
- introducing a discretionary and prior right to object;
- providing a discretionary right to have personal data erased from training datasets;
- putting in place mechanisms to allow individuals to be identified when they exercise their rights;
- facilitating the communication of rights and actively notifying users about updates to datasets or models, etc.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 8
Step 3 (bis): Adapt safeguards to data scraping
The principle
Web scraping is not, in itself, prohibited under the GDPR. If you are a private body, you may rely on the legal basis of legitimate interest to resort to it, provided that you implement appropriate safeguards.
In practice
Respect the principle of data minimization
To this end, you should:
- Define in advance what you are looking for: clearly determine which categories of data are relevant before starting the collection process.
- Do not collect more than necessary: exclude the collection of certain types of data, either through filtering or by excluding specific types of websites, especially sensitive data, if it is not relevant to the intended processing.
- Delete irrelevant data: if you inadvertently collect data that is not relevant, it must be deleted immediately.
- Respect websites that prohibit automated data collection: you must not collect data from websites that oppose scraping through technical protections (such as CAPTCHAs or robots.txt files).
Respect reasonable expectations
You must take into account the public accessibility of the data, the nature of the source websites (e.g., social media platforms, online forums), and the type of publication (such as a blog post freely accessible to all versus content behind restrictions), etc.
Moreover, web scraping does not fall within individuals’ reasonable expectations when the website in question explicitly opposes the scraping of its content through technical protections (such as CAPTCHAs or robots.txt files).
Additional safeguards
You may implement additional safeguards depending on the intended use of your AI system. One or more of these measures may be necessary based on the risks associated with the processing:
- Establish a default exclusion list of websites that contain particularly sensitive data (e.g., health-related forums);
- Exclude websites that oppose the scraping of their content through technical or legal means (e.g., terms of service);
- Limit data collection to freely accessible content (without requiring account creation), where individuals are aware of the public nature of their data;
- Inform individuals as widely as possible (e.g., through online articles, social media posts, etc.);
- Provide a discretionary and advance right to object, before data collection begins, with a reasonable delay before model training;
- Anonymize or pseudonymize the data immediately after collection, and prevent any re-identification through user identifiers.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 8 bis
Step 4: Check if you can re-use certain personal data
The principle
If you plan to re-use a dataset that contains personal data, make sure it is legal. That depends on the method of collection and the source of the data in question. As a data controller (see “Step 2: Determine your responsibilities”), you must carry out certain additional checks to ensure that such use is lawful.
In practice
The rules will depend on the situation.
The provider reuses data that it has already collected itself
You may want to re-use the data you originally collected for another purpose. In this case, if you had not foreseen and informed the data subjects about this re-use, you should check that this new use is compatible with the original purpose, unless you are authorised by the data subjects (they have consented) or by a text (e.g. a law, decree etc.).
You must carry out what is known as a “compatibility test”, which must take into account:
- the existence of a link between the initial objective and that of building a dataset for training an AI system;
- the context in which the personal data were collected;
- the type and nature of the data;
- the possible consequences for the persons concerned;
- the existence of appropriate safeguards (e.g. pseudonymisation of data).
The provider re-uses publicly available data (open source)
In this case, you need to make sure that you are not re-using a dataset whose constitution was manifestly unlawful (e.g. from a data leak). A case-by-case analysis must be carried out.
The CNIL recommends that re-users check and document (for example, in the data protection impact assessment) the following:
- the description of the dataset mentions their source;
- the establishment or dissemination of the dataset is not manifestly the result of a crime or offense or has been the subject of a public conviction or sanction by a competent authority which has involved a removal or prohibition of exploitation;
- there is no glaring doubt that the dataset is lawful by ensuring in particular that the conditions for data collection are sufficiently documented;
- the dataset does not contain sensitive data (e.g. health data or data revealing political opinions) or infringement data or, if it does, it is recommended to carry out additional checks to ensure that such processing is lawful.
The body that uploaded the dataset is supposed to have ensured that the publication complied with the GDPR, and is responsible for it. However, you do not have to verify that the bodies that set up and disseminated the dataset have complied with all the obligations laid down in the GDPR: the CNIL considers that the four verifications mentioned above are generally sufficient to allow the re-use of the dataset for the training of an AI system, provided that the other CNIL recommendations are complied with. If you receive information, especially from people whose data is contained in the dataset, that highlights problems with the lawfulness of the data used, you will need to investigate further.
The provider reuses data acquired from a third party (data brokers, etc.)
For the third party sharing personal data, sometimes for remuneration, there are two types of situations.
The third party collected the data for the purpose of building a dataset for AI system training. It must ensure that the data transmission processing complies with the GDPR (definition of an explicit and legitimate objective, requirement of a legal basis, information to individuals and management of the exercise of their rights, etc.).
The third party did not initially collect the data for that purpose. It must then ensure that the transmission of those data pursues an objective compatible with that which justified their collection. It will therefore have to carry out the “compatibility test” described above.
The re-user of the data has several obligations:
- It must ensure that it is not re-using a manifestly unlawful dataset by carrying out the same checks as those set out in the section above. The conclusion of an agreement between the original data holder and the re-user is recommended in order to facilitate these verifications.
- In addition to these checks, it must ensure its own compliance with the GDPR when processing this data.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 4
Step 5: Minimize the personal data you use
The principle
The personal data collected and used must be adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary in the light of the objective defined: this is the principle of data minimisation. You must respect this principle and apply it rigorously when the data processed is sensitive (data concerning health, concerning sex life, religious beliefs or political opinions, etc.).
In practice
The method to be used
You should focus on the technique that achieves the desired result (or of the same order) using as little personal data as possible. In particular, the use of deep learning techniques should therefore not be systematic.
The choice of the learning protocol used may, for example, make it possible to limit access to data only to authorised persons, or to give access only to encrypted data.
Selection of strictly necessary data
The principle of minimisation does not prohibit the training of an algorithm with very large volumes of data, but implies:
- to have an upstream reflection in order to have recourse only to personal data useful for the development of the system; and
- to subsequently implement the technical means to collect only these ones.
The validity of design choices
In order to validate the design choices, it is recommended as a good practice to:
- conduct a pilot study, i.e. carry out a small-scale experiment. Fictitious, synthetic, anonymised data may be used for this purpose;
- question an ethics committee (or an "ethical advisor"). This committee must ensure that ethical issues and the protection of the rights and freedoms of individuals are properly taken into account. It can thus formulate opinions on all or part of the organisation’s projects, tools, products, etc. likely to raise ethical issues.
The organisation of the collection
You must ensure that the data collected is relevant in view of the objectives pursued. Several steps are strongly recommended :
- Data cleaning: This step allows you to build a quality dataset and thus strengthen the integrity and relevance of the data by reducing inconsistencies, as well as the cost of learning.
- Identification of the relevant data: This step aims to optimize system performance while avoiding under- and over-fitting. In practice, it allows you to make sure that certain classes or categories that are unnecessary for the task at hand are not represented, that the proportions between the different interest classes are well balanced, etc. This procedure also aims to identify data that is not relevant for learning (which will then have to be removed from the dataset).
- The implementation of measures to incorporate the principles of personal data protection by design: This step allows you to apply data transformations (such as generalisation and/or randomisation measures, data anonymisation, etc.) to limit the impact on people.
- Monitoring and updating of data: minimisation measures could become obsolete over time. The data collected could lose their exact, relevant, adequate and limited characteristics, due to a possible drift of the data, an update thereof or technical developments. You will therefore have to conduct a regular analysis to ensure the follow-up of the constituted dataset.
- Documentation of the data used for the development of an AI system: it allows you to guarantee the traceability of the datasets used which the large size can make difficult. You must keep this documentation up-to-date as the dataset evolves. The CNIL provides here a model of documentation.
- For more information, see the how-to sheet 6 and the how-to sheet 7
Step 6: Set a retention period
The principle
Personal data cannot be kept indefinitely. The GDPR requires you to define a period of time after which data must be deleted or, in some cases, archived. You must determine this retention period according to the purpose that led to the processing of these data.
In practice
You must set a retention period for the data used for the development of the AI system:
- For the development phase: Data retention needs to be pre-planned and monitored over time. Data subjects must be informed of the data retention period (e.g. in the information notices);
- For the maintenance or improvement of the product: where the data no longer need to be accessible for the day-to-day tasks of the persons in charge of the development of the AI system, it should in principle be deleted. However, they can be kept for the maintenance of the product or its improvement if guarantees are implemented (partitioned support, restriction of access only to authorized persons, etc.).
- For more information, see how-to sheet 7
Step 7: Inform individuals
The principle
You must inform the individuals concerned so that they understand how their data will be used (why, how, and in what manner) and are able to exercise their rights (such as the rights to object, access, and rectification).
This information obligation applies both to data collected directly from individuals (e.g., as part of a service provision or a contractual relationship with voluntary participants) and to data collected indirectly, including through web scraping.
In practice
Ensure accessibility of the information
You must ensure that the information provided is easily accessible:
- individual-level information may be included directly on the data collection form, via a pre-recorded voice message, etc;
- general information may be published on your website as part of a privacy notice.
It is recommended to allow a reasonable delay between the information of individuals about the data collection and the training of the AI model, due to the difficulty individuals may face in exercising their rights once the model has been trained.
Ensure clarity and intelligibility of the information
You must ensure that the information is concise and clear. The complexity of AI systems should not prevent individuals from understanding how their data is used.
It is recommended to explain, using diagrams, for example, how data is used during training, how the developed AI system works, and how to distinguish between the training dataset, the AI model, and the model’s outputs.
Choosing between individual and general information
As a rule, individuals must be provided with individual-level information, but the GDPR allows for certain exceptions:
- all relevant information about the processing has already been provided to the data subject (e.g., by a third party).
- providing the information would require disproportionate effort, taking into account the effort involved (e.g., lack of contact details, age of the data) and the level of intrusion into privacy. In particular, individual notification is often considered disproportionate when pseudonymized data is collected via web scraping, as identifying and contacting individuals may require collecting additional or more identifiable data.
In such cases, you may publish a comprehensive general information notice on your website instead.
Please note: article 53 of the AI Act requires providers of general-purpose AI models to complete a public summary of the content used to train the AI system, based on a template provided by the AI Office. This summary may may contribute to the general information about data sources.
Specific information to be provided
In general, you must provide all the information required under Articles 13 and 14 of the GDPR. However, when developing artificial intelligence systems, some specific considerations apply.
-
Information about data sources
Providing information on data sources presents particular challenges. Two main cases should be distinguished :
- If the number of sources is limited: you are generally required to provide the precise identity of those sources. This applies, for example, to web scraping carried out on a limited number of websites.
- If you use a large number of sources: you may instead indicate the categories of sources, including the names of some main or representative examples. This is relevant in cases where web scraping involves a vast number of sources.
-
Informing individuals about the inability to identify them
Where applicable, you must inform data subject of the impossibility to identify them, including for the purpose of responding to data subject rights requests (Article 11 of the GDPR). Where possible, the CNIL recommends indicating what additional information individuals may provide to help facilitate their identification if they wish to exercise their rights.
-
The specific case of AI models subject to the GDPR
Where your AI model or system is subject to the GDPR, the CNIL recommends clearly stating the nature of the risk related to the extraction of personal data from the training dataset through manipulation of the AI model alone, the measures implemented to mitigate these risks, the available redress mechanisms if such risks materialize.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 9
Step 8: Ensure the exercise of data subject rights
The principle
Individuals must be able to exercise their rights (rights of access, rectification, erasure, restriction of processing, and data portability) in relation to both the training dataset and the AI model itself, if the model is not considered anonymous.
The solutions you implement to ensure these rights must be realistic and proportionate. While AI systems pose specific challenges (such as identifying a natural person within a large dataset or within a model, etc.), these challenges must not prevent the implementation of appropriate responses.
The CNIL recommends that you inform the data suject of the outcome of their rights request, particularly when changes made to the dataset do not immediately affect the trained AI system.
In practice
Difficulties in identifying the data subject
If you can demonstrate that it is not possible to identify the data subject within the training dataset or the AI model, you must indicate this in your response to a rights request. You are not required to collect additional personal data solely for the purpose of responding to the request.
When the GDPR applies to the model, two scenarios can be distinguished:
- in some cases, the presence of personal data in the model is obvious (for example, some AI models are designed to output personal data);
- in others, you may be able to demonstrate that it is not possible to identify individuals within your model. Based on the current state of the art, it is generally not possible to identify all personal data memorized by an AI model that belongs to a particular individual.
However, individuals may choose to provide additional personal data to help find their information within the dataset or the model (e.g., an image or a pseudonym). The CNIL recommends anticipating these difficulties and informing individuals of the types of additional information that could assist them in their requests.
Regarding models specifically:
- if you still have access to the training dataset, identifying the individual within it is relevant to assess whether personal data may have been memorized by the model;
- otherwise, the nature of the data used allows you to anticipate which categories of data are more likely to have been memorized, thereby facilitating identification attempts. In the case of generative AI models, an internal procedure to query the model may be implemented.
Regarding the right of access
In the case of a training dataset
The right of access allows any individual to obtain, free of charge, a copy of all personal data processed about them. This disclosure must not infringe on the rights and freedoms of others (such as the rights of other data subjects, intellectual property rights, trade secrets of the dataset holder, etc.).
You must provide all the information required by the GDPR when an individual exercises its right of access. In particular, data subjects must be able to:
- identify the specific recipients of their data;
- know the source of the data when it was not collected directly from them (e.g., data brokers).
When the data was not collected directly from the data subject (for example, if it was provided by a data broker), the right of access includes any “available” information regarding its source.
In the case of an AI model subject to the GDPR
Two situations may arise :
- If you identify the data subject and confirm that their personal data has been memorized by the model, you must inform the individual of this. You should provide the results of your investigation, including, in the case of generative AI systems, any outputs that contain their personal data.
- If you cannot verify whether their data has been memorized, but also cannot rule it out (due to current technical and scientific limitations), the CNIL recommends informing individuals that it is not impossible that training data related to them may have been memorized by the model. In this case, you must also provide the following additional information: the recipients of the model, the retention period or the criteria used to determine it, the rights that can be exercised over the model and its origin, if you are not its developer.
Rights to rectification, erasure, and objection
Individuals have, under certain conditions, the right to rectify their data, to have it erased, and to object to its processing on grounds relating to their particular situation whether the data is part of a training dataset or used within an AI model.
The exercise of rights over an AI model is not absolute. The proportionality of the measures described below depends on the sensitivity of the data, the risks posed to individuals by potential regurgitation or disclosure of their data or the impact on the organization’s freedom of enterprise.
By default, exercising data subject rights over an AI model requires retraining the model, provided you still hold the training data. Retraining may be performed periodically to address multiple requests at once, and may take up to three months, depending on the complexity and volume of requests. Data subjects must be informed of the expected timeline. An updated version of the model must be shared with its users, with contractual provisions requiring that only regularly updated versions be used.
If you can demonstrate that retraining is disproportionate, it is recommended to implement alternative measures, such as filters applied around the AI system that encapsulate the model, if you can show these measures are sufficiently effective and robust.
Where possible, it is recommended to implement general rules for detecting and pseudonymizing the personal data concerned rather than relying on a simple blacklist.
Finally, under the GDPR, each recipient to whom personal data has been disclosed must be notified of any rectification or erasure, unless such notification proves impossible or involves disproportionate effort. The use of APIs or download traceability mechanisms can help facilitate this communication. You may also implement contractual obligations requiring downstream propagation of data subject rights, e.g., through reuse licenses.
Exemptions from data subject rights requests
You may refuse to comply with a data subject rights request when the request is manifestly unfounded or excessive, when the exercise of one or more rights is excluded by French or European law or when the processing is carried out for statistical, scientific research, or historical research purposes.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 10
Step 9: Securing your AI system
The principle
The GDPR requires data controllers to implement appropriate security measures: infrastructure management and dimensioning, access authorizations, backup management, and physical security.
AI systems must undergo a risk analysis, with particular attention paid to software development, the creation and management of training datasets, and system maintenance.
The CNIL recommends conducting a DPIA (Data Protection Impact Assessment) to document the security measures (see “Focus: Conducting a DPIA”).
In practice
Security measures specific to the development of an AI system
| Security goals | Security measures to consider |
|---|---|
| Ensure the confidentiality and integrity of training data |
Check the reliability, quality, and integrity of training data sources and their annotations throughout the entire lifecycle Log and manage dataset versions Use synthetic or dummy data when possible (for security testing, integration, certain audits, etc.) Encrypt backups and communications Control access to data when it is not published as open source Anonymize or pseudonymize the data Segregate sensitive datasets Prevent loss of control over data through organizational measures |
| Guarantee the performance and integrity of the AI system |
Incorporate data protection considerations into system design choices, with an emphasis on data minimization (see “Step 5: Minimize data”) Use verified development tools, libraries, and pre-trained models. Particular attention should be paid to the potential presence of backdoors in the system Favor verified import and storage formats (e.g., safetensors) Use a controlled, reproducible, and easily deployable development environment Implement a continuous development and integration process Document the system design and functionality, including required hardware, implemented protection measures, etc. Conduct internal or third-party security audits, including simulated common attacks on the AI system (see “Step 10: Assessing the status of an AI model”) |
| Anticipate how the system will work |
Inform users of the system's limitations in lab settings and in its intended use contexts Provide users with sufficient information to help them interpret the outputs Ensure the possibility to shut down the system Control AI outputs using filters, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), or digital watermarking techniques |
General security measures
The functionality of AI systems generally depends on the models used, but the most likely risks today relate to other components of the system (such as backups, interfaces, and communications). It may therefore be easier for an attacker to exploit a vulnerability in the software to access training data than to carry out a membership inference attack.
You must therefore ensure that general security measures for information systems are properly implemented. These measures and the risks they address are described in the CNIL’s practice guide for the security of personal data.
- For more information, see how-to sheet 10
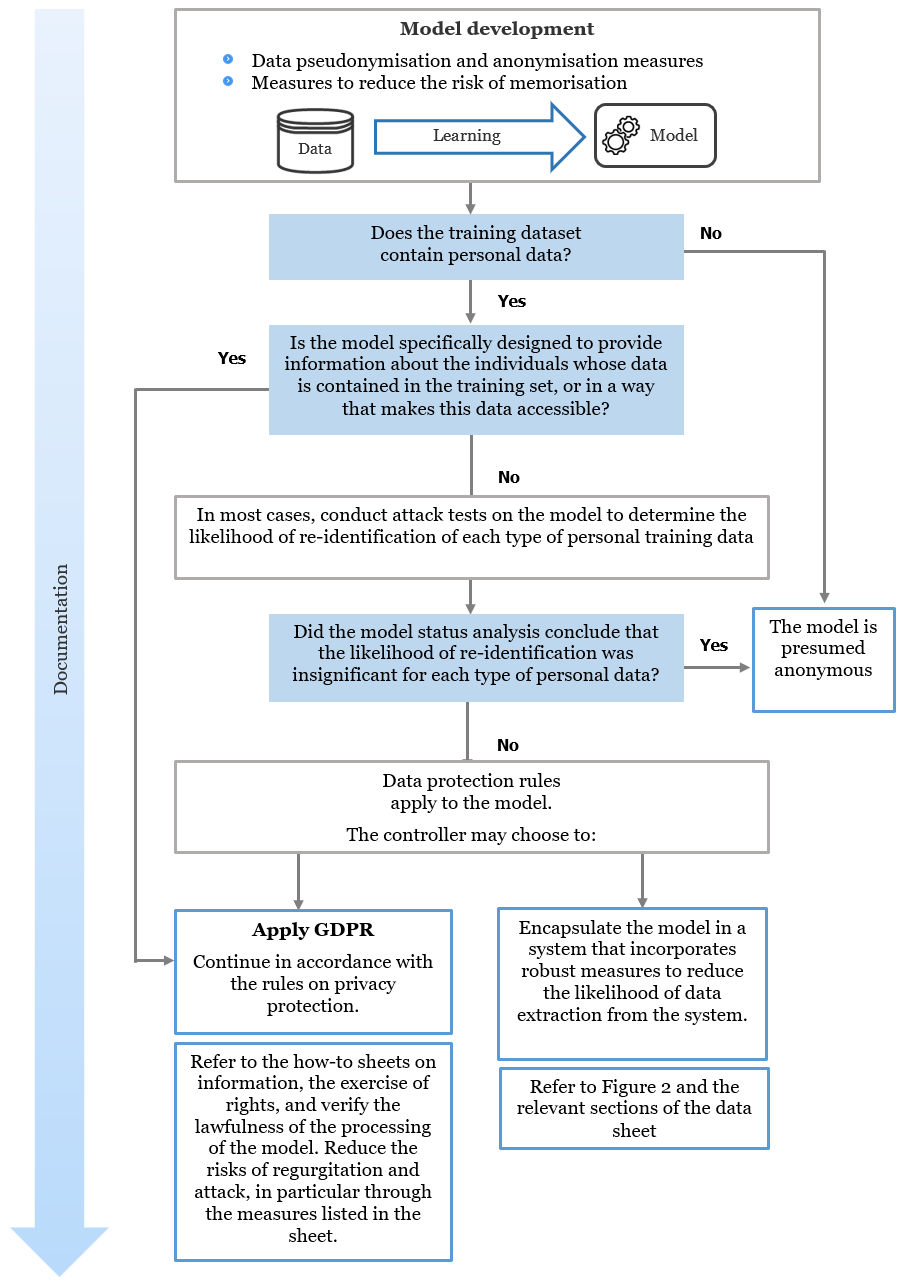
Step 10: Assessing the status of an AI model
The principle
An AI model is a statistical representation of the characteristics of the dataset on which it was trained. Numerous academic studies have shown that, in certain cases, this representation is detailed enough to lead to disclosure of training data. As stated in EDPB Opinion 28/2024, AI models trained on personal data must, in most cases, be considered subject to the GDPR.
To determine whether your model falls under the scope of the GDPR (and can thus be considered anonymous or not), you must conduct an assessment of its status. This assessment aims to extract personal data from the model using means that are reasonably likely to be used (including re-identification attack tests).
In practice
What steps should be taken to determine whether the GDPR applies to an AI model?
The diagram below outlines the steps to determine whether the GDPR applies to your model or whether it can be considered anonymous.
When should re-identification attack tests be conducted on a model?
A set of indicators can help you assess the need to conduct re-identification attacks on your model’s training data:
- regarding the training data: if the data is identifiable and precise, heterogeneous, rare, or duplicated in the dataset;
- Regarding the model architecture: if there is a high ratio between the number of parameters and the size of the training data, a risk of overfitting, or a lack of confidentiality guarantees during training (e.g., differential privacy, etc.);
- Regarding the model’s features and use cases: if the objective is to reproduce data similar to the training data (e.g., content generation in the case of generative AI), or if re-identification attacks have been successfully carried out on similar models.
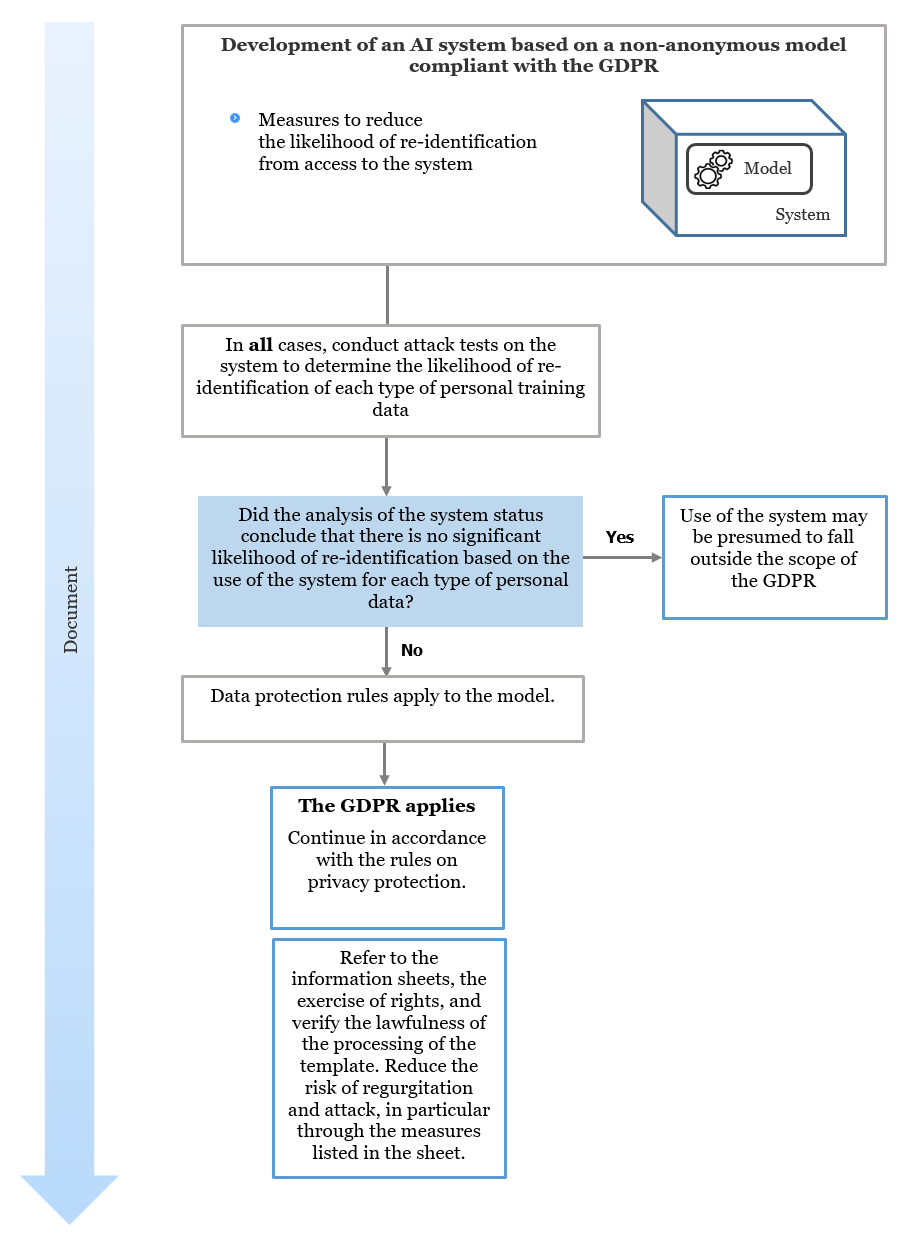
What steps should be taken to determine whether the GDPR applies to a system?
If the analysis of your model’s status has concluded that it cannot be considered anonymous, you may reduce the likelihood of re-identifying individuals by embedding the model within an AI system that implements robust measures to prevent data extraction.
In some cases, these measures, which must be tested through systematic attacks on the system, may allow the use of the system to fall outside the scope of the GDPR. These measures may include (though they are not necessarily sufficient):
- making access to or retrieval of the model impossible,
- implementing access restrictions to the system,
- limiting the precision or filtering the outputs of the model,
- applying security measures (see “Step 9: Securing your AI system”).
The diagram below outlines the approach you should follow to determine this:
- For more information, see how-to sheet 13
Step 11: Comply with GDPR principles during the annotation phase
The principle
Annotation involves assigning a description, known as a "label" or "tag", to each data item that will serve as the “ground truth” for the model to learn how to process, classify, or distinguish data based on this information.
In practice
Implement the data minimization
Your data annotation must be limited to what is necessary and relevant for training the model and for the intended functionality. It may include data that is indirectly related to the system’s functionality if its impact on performance is demonstrated (empirically or theoretically) or reasonably plausible. It can also include information useful for performance measurement, error correction, or bias evaluation, by providing contextual elements (e.g., weather, date, time, etc.).
This principle also applies to annotations from previously collected data, purchased datasets, or datasets downloaded from open sources or third parties. If technical constraints prevent you from applying this principle fully, you must be able to justify your efforts to use the most relevant annotated dataset and to remove irrelevant annotations.
Annotations must also be limited to what is necessary for training the model. The recommendations in “Step 5: Minimize the personal data you use” also apply here.
Ensure the accuracy principle
The annotations you create must be accurate, objective, and, where possible, up to date. If not, the system’s potential reproduction of these annotations may lead to inaccurate, degrading, or discriminatory outputs.
Annotation involving sensitive data
"Sensitive" annotation refers to an annotation that includes sensitive data as defined by Article 9 of the GDPR, even if the training data it refers to is not itself sensitive. As a rule, "sensitive" annotation is prohibited under that same article.
However, exceptions may apply for example, conducting health research projects using data collected during medical care, through a commitment to comply with a reference methodology (Article 66 of the French Data Protection Act –LIL) or with prior authorization granted by the CNIL. In such cases, you must implement specific safeguards:
- Annotate using objective and factual criteria (e.g., skin color as pixel color rather than ethnic origin), limit yourself strictly to the information present in the data, without interpretation, increase the security of the annotated data and et assess the risks of data regurgitation and inference.
Information for individuals
In addition to the mandatory information mentioned in “Step 7: Informing individuals”, the CNIL recommends providing the following information as best practice:
- The objectives of the annotation (e.g., identifying individuals in an image);
- If it is not you, the organisation in charge of the annotation, as well as the social responsibility criteria respected within the framework of a contract binding a person in charge of the annotation to the data controller, particularly when the annotation concerns data that may be offensive;
- The security measures taken during the annotation phase.
If the annotation is likely to have consequences for the individual in the event of a data leak or if their data represents a significant part of the training database, the CNIL recommends informing individuals of the result of the annotation after the fact, where possible.
The exercise of rights over annotations is detailed in "Step 8: Ensuring the exercise of data subject rights".
- For more information, see how-to sheet 11
Focus: Carry out a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
The principle
The Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is an approach that allows you to map and assess the risks of processing personal and establish an action plan to reduce them to an acceptable level. In particular, it will lead you to define the security measures needed to protect the data.
In practice
Achieving a DPIA for the development of AI systems
It is strongly recommended to carry out a DPIA for the development of your AI system, especially when two of the following criteria are met:
- sensitive data are collected;
- personal data are collected on a large scale;
- data of vulnerable persons (minors, persons with disabilities, etc.) are collected;
- datasets are crossed or combined;
- new technological solutions are implemented or innovative use is made.
In addition, if significant risks exist (e.g.: data misuse, data breach, or discrimination), a DPIA must be carried out even if two of the above criteria are not met.
To help carry out a DPIA, the CNIL makes available the dedicated open source PIA software.
The risk criteria introduced by the EU AI Act
The CNIL considers that, for the development of high-risk systems covered by the AI Act and involving personal data, the performance of a DPIA is in principle necessary.
The scope of the DPIA
There are two types of situations for the provider of an AI system, depending on the purpose of the AI system (see “Step 1: Define an objective (purpose) for the AI system”).
You clearly know what the operational use of your AI system will be
It is recommended to carry out a general DPIA for the whole life cycle, which includes the development and deployment phases. Please note that if you are not the user/deployer of the AI system, it is this actor that will be responsible for carrying out the DPIA for the deployment phase (although it may be based on the DPIA model you have proposed).
If you are developing a general purpose AI system
You will only be able to carry out a DPIA for the development phase. This DPIA should be provided to the users of your AI system to enable them to conduct their own analysis.
AI risks to be considered in a DPIA
Processing of personal data based on AI systems presents specific risks that you must take into account:
- the risks related to the confidentiality of data that can be extracted from the AI system;
- the risks to data subjects linked to misuse of the data contained in the training dataset (by your employees who have access to it or in the event of a data breach);
- the risk of automated discrimination caused by a bias in the AI system introduced during development;
- the risk of producing false fictitious content on a real person, in particular in the case of generative AI systems;
- the risk of automated decision-making when the staff member using the system is unable to verify his performance in real conditions or to take a decision different to the one provided by the system without detriment (due to hierarchical pressure, for example);
- the risk of users losing control over their data published and freely accessible online;
- the risks related to known attacks, specific to AI systems (e.g. data poisoning attacks);
- the systemic and serious ethical risks related to the deployment of the system.
Actions to be taken based on the results of the DPIA
Once the level of risk has been determined, your DPIA must provide for a set of measures to reduce it and keep it at an acceptable level, for example:
- security measures (e.g. homomorphic encryption or the use of a secure execution environment);
- minimisation measures (e.g. use of synthetic data);
- anonymisation or pseudonymisation measures (e.g. differential privacy);
- data protection measures from the outset (e.g. federated learning);
- measures facilitating the exercise of rights or redress for individuals (e.g. machine unlearning techniques, explainability and traceability measures regarding the outputs of the system, etc.);
- audit and validation measures (e.g. fictitious attacks).
Other, more generic measures may also be applied: organisational measures (management and limitation of access to the datasets which may allow a modification of the AI system, etc.), governance measures (establishment of an ethics committee, etc.), measures for the traceability of actions or internal documentation (information charter, etc.).
- For more information, see how-to sheet 5